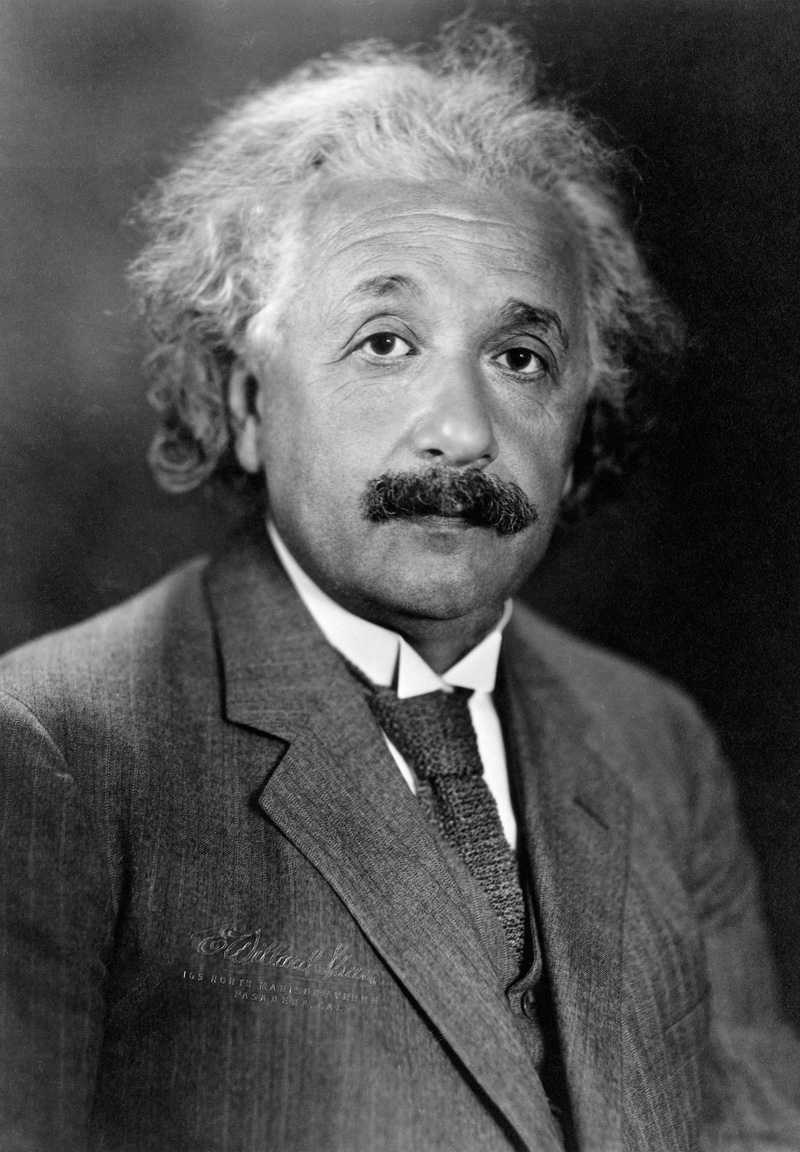Difference between revisions of "IMAGES"
m |
m |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
<div class="col-md-5"><p>We use the metaphor of the [[magical mirror]] (or simply "Mirror") to mark the entry point to an emerging academic reality (and paradigm, and frontier). To understand its meaning, bring to mind that the traditional idea of what constitutes "good" knowledge and knowledge work, as represented by the standards of excellence in the sciences: We are first of <em>disciplined</em> to adhere to the language and the methods of an established discipline (by becoming "philosophy doctors"). Beyond that, we are expected to assume the attitude of impartial, disinterested or "objective" observers. </p> | <div class="col-md-5"><p>We use the metaphor of the [[magical mirror]] (or simply "Mirror") to mark the entry point to an emerging academic reality (and paradigm, and frontier). To understand its meaning, bring to mind that the traditional idea of what constitutes "good" knowledge and knowledge work, as represented by the standards of excellence in the sciences: We are first of <em>disciplined</em> to adhere to the language and the methods of an established discipline (by becoming "philosophy doctors"). Beyond that, we are expected to assume the attitude of impartial, disinterested or "objective" observers. </p> | ||
| − | <p>The Mirror symbolizes a deep insight, leading to a radical change of self-identity, attitude and values. "When we see ourselves in the Mirror", reads the explanation of this [[ideogram]], we see the same world that we see around us. But we also see ourselves in the world. A profound insight results: We are not | + | <p>The Mirror symbolizes a deep insight, leading to a radical change of self-identity, attitude and values. "When we see ourselves in the Mirror", reads the explanation of this [[ideogram]], "we see the same world that we see around us. But we also see ourselves in the world. A profound insight results: We are not those objective observes we believed we were, hovering above the world and taking snapshots through the objective of the scientific method. We are <em>in</em> the world! The scientific method is our own creation. Also so is the world we see around us, it is increasingly our own creation. We are <em>responsible</em> for that creation!"</p> |
<p>As the case was in the Louis Carroll's story from which this metaphor has been borrowed, one can also walk through the Mirror. And when one does, one finds himself in an academic reality which is surprisingly often the reverse image of the academic reality we are accustomed to.</p> | <p>As the case was in the Louis Carroll's story from which this metaphor has been borrowed, one can also walk through the Mirror. And when one does, one finds himself in an academic reality which is surprisingly often the reverse image of the academic reality we are accustomed to.</p> | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
<div class="col-md-3"><h4>– Physical concepts are free creations of the human mind, and are not, however it may seem, uniquely determined by the external world.</h4></div> | <div class="col-md-3"><h4>– Physical concepts are free creations of the human mind, and are not, however it may seem, uniquely determined by the external world.</h4></div> | ||
| − | <div class="col-md-6"><p>There are far too many [[giants]] on whose shoulders we may stand to see the Mirror. Hence we here represent them by a single one, Albert Einstein. Also elsewhere on these pages Einstein | + | <div class="col-md-6"><p>There are far too many [[giants]] on whose shoulders we may stand to see the Mirror. Hence we here represent them by a single one, Albert Einstein. Also elsewhere on these pages Einstein appears in the role of an icon for "modern science". "Physical concepts are free creations of the human mind, and are not, however it may seem, uniquely determined by the external world," Einstein and Infeld wrote in Evolution of Physics. "In our endeavor to understand reality we are somewhat like a man trying to understand the mechanism of a closed watch. He sees the face and the moving hands, even hears its ticking, but he has no way of opening the case. If he is ingenious he may form some picture of a mechanism which could be responsible for all the things he observes, but he may never be quite sure his picture is the only one which could explain his observations. He will never be able to compare his picture with the real mechanism and he cannot even imagine the possibility or the meaning of such a comparison."</p> |
<p>So we've just heard 'modern science' tell us that the "correspondence with reality" is something that is just simply impossible to verify! And now we'll hear it say that it is also a common result of illusion: "During philosophy’s childhood it was rather generally believed that it is possible to find everything which can be known by means of mere reflection. (...) Someone, indeed, might even raise the question whether, without something of this illusion, anything really great can be achieved in the realm of philosophical thought– but we do not wish to ask this question. This more aristocratic illusion concerning the unlimited penetrative power of thought has as its counterpart the more plebeian illusion of naïve realism, according to which things “are” as they are perceived by us through our senses. This illusion dominates the daily life of men and animals; it is also the point of departure in all the sciences, especially of the natural sciences.” </p> | <p>So we've just heard 'modern science' tell us that the "correspondence with reality" is something that is just simply impossible to verify! And now we'll hear it say that it is also a common result of illusion: "During philosophy’s childhood it was rather generally believed that it is possible to find everything which can be known by means of mere reflection. (...) Someone, indeed, might even raise the question whether, without something of this illusion, anything really great can be achieved in the realm of philosophical thought– but we do not wish to ask this question. This more aristocratic illusion concerning the unlimited penetrative power of thought has as its counterpart the more plebeian illusion of naïve realism, according to which things “are” as they are perceived by us through our senses. This illusion dominates the daily life of men and animals; it is also the point of departure in all the sciences, especially of the natural sciences.” </p> | ||
Revision as of 09:53, 23 July 2018
Contents
- 1 Federation Through Images
- 1.1 Not all images are worth one thousand words.
- 1.2 – Eppur si muove!
- 1.3 – On every university campus there is a Mirror.
- 1.4 – Physical concepts are free creations of the human mind, and are not, however it may seem, uniquely determined by the external world.
- 1.5 – [The] flow from the theoretical to the conventional is an adjunct of progress in the logical foundations of any science.
- 1.6 Once we acknowledge as legitimate the view that the scientific language and method have been our own creation, and that they have limited what we are able to see and assert, it becomes legitimate to also create a language and a method that allows us to see and say more.
- 1.7 – [T]he nineteenth century developed an extremely rigid frame for natural science which formed not only science but also the general outlook of great masses of people.
- 1.8 – Whatever we cannot speak of, we need to be silent about (find proper quotation).
- 1.9 – Short Whorf's quotation.
- 1.10 – The mind must be available to attend to any theme that presents itself to it.
- 1.11 Ingress
- 1.12 – Enough of this. Newton, forgive me...
- 1.13 Ingress.
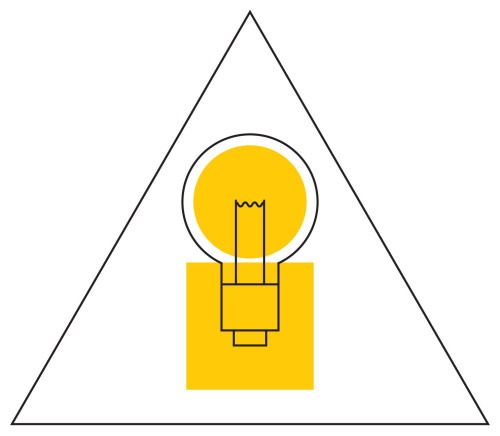
- 1.14 The task of Knowledge Federation is to prototype and evolve a socio-technical 'light bulb'.
Federation Through Images
Not all images are worth one thousand words.
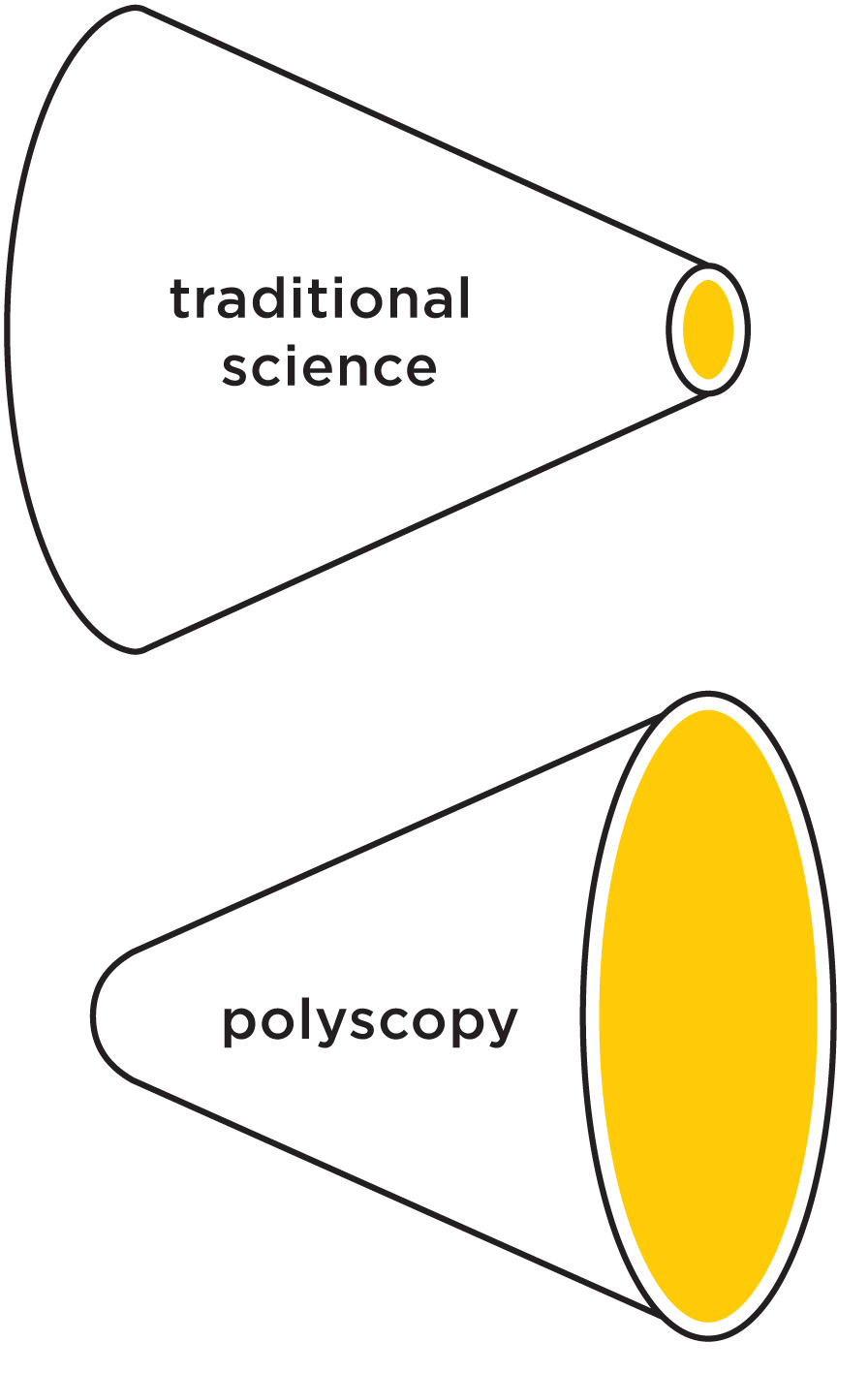
But the ideograms are! They play a similar role in knowledge federation as mathematical formulas do in traditional science. An ideogram can condense a wealth of insights and many pages of text into an image whose message can be recognized at a glance. Recall the Newton's formula, or Einstein's ubiquitous E=mc² – those are already ideograms! But the possibilities behind the ideographic approach are endless and vastly surpass the conventional maths. Those possibilities vastly surpass also what is demonstrated by our illustrations; they are yet to be developed through creative use of new media.
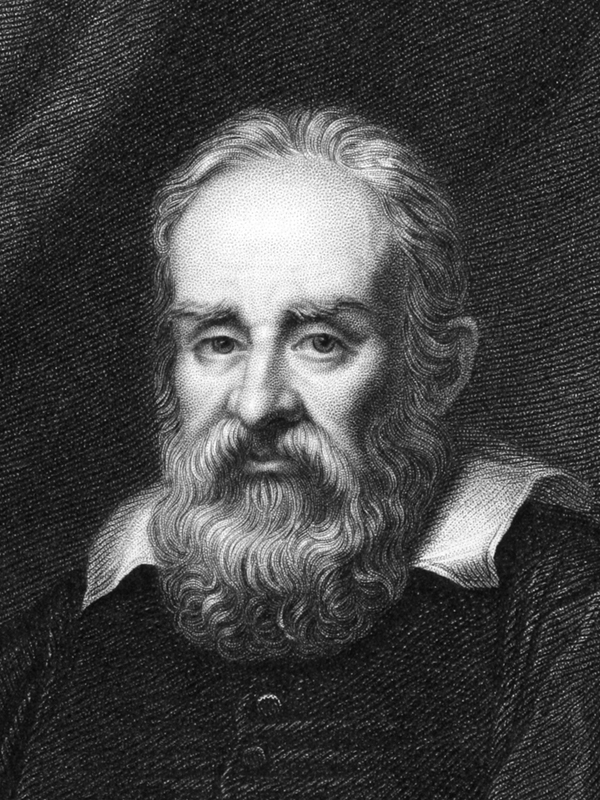
– Eppur si muove!
To see that the theme we are talking about is not at all "of philosophical interest" (only), think about the world of the Late Middle Ages: never-ending wars, horrifying epidemics, infamous Inquisition trials... Bring to mind the iconic image of Galilei in house prison, a century after Copernicus, whispering "Eppur si muove!" into his beard. The problems of the day were not solved by focusing on those problems, but by a slow and steady development of a whole new approach to knowledge. Several centuries of unprecedented progress followed. Could a similar advent be in store for us today?
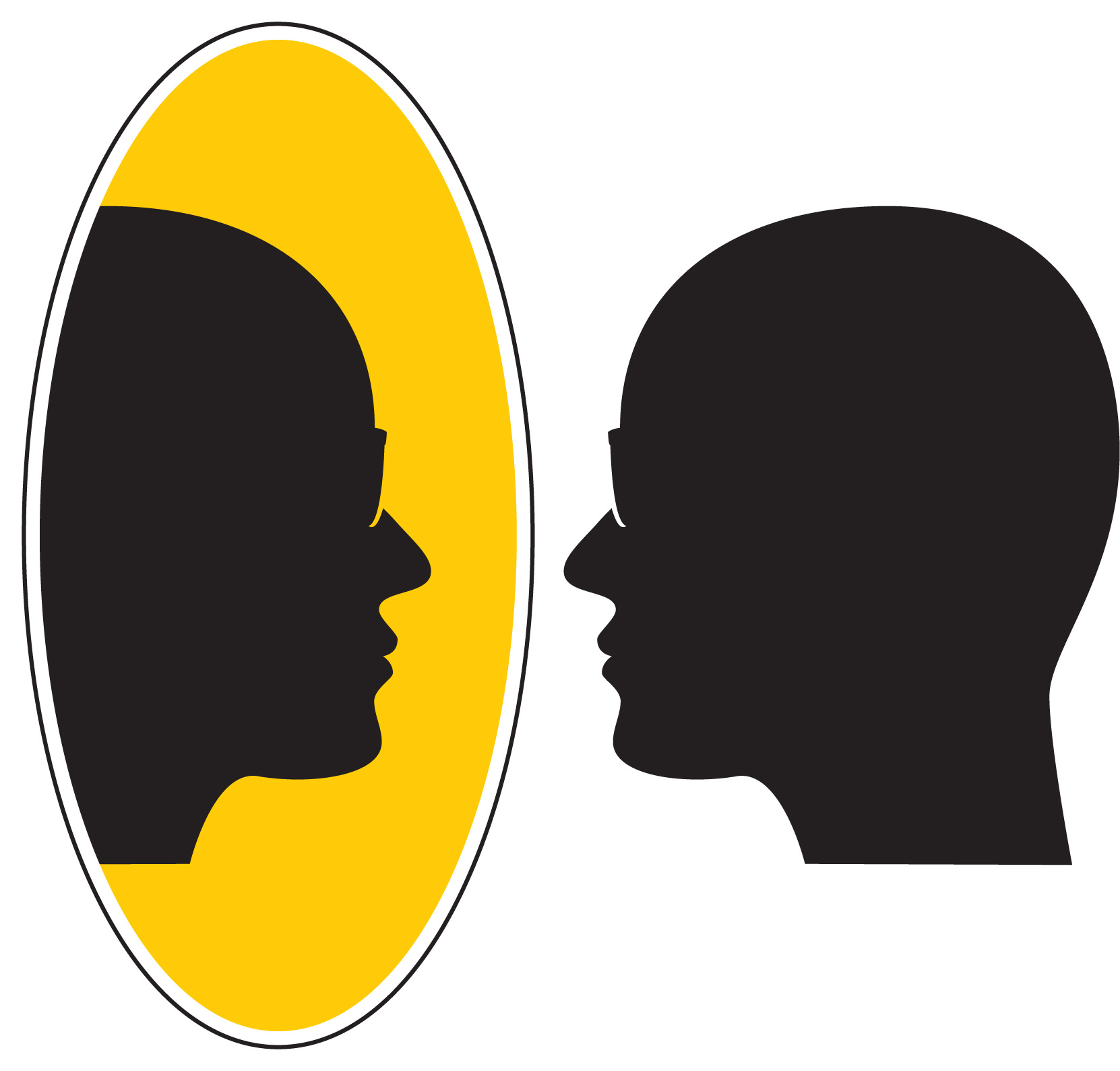
– On every university campus there is a Mirror.
We use the metaphor of the magical mirror (or simply "Mirror") to mark the entry point to an emerging academic reality (and paradigm, and frontier). To understand its meaning, bring to mind that the traditional idea of what constitutes "good" knowledge and knowledge work, as represented by the standards of excellence in the sciences: We are first of disciplined to adhere to the language and the methods of an established discipline (by becoming "philosophy doctors"). Beyond that, we are expected to assume the attitude of impartial, disinterested or "objective" observers.
The Mirror symbolizes a deep insight, leading to a radical change of self-identity, attitude and values. "When we see ourselves in the Mirror", reads the explanation of this ideogram, "we see the same world that we see around us. But we also see ourselves in the world. A profound insight results: We are not those objective observes we believed we were, hovering above the world and taking snapshots through the objective of the scientific method. We are in the world! The scientific method is our own creation. Also so is the world we see around us, it is increasingly our own creation. We are responsible for that creation!"
As the case was in the Louis Carroll's story from which this metaphor has been borrowed, one can also walk through the Mirror. And when one does, one finds himself in an academic reality which is surprisingly often the reverse image of the academic reality we are accustomed to.
Knowledge federation may now be understood as a model or a prototype of that other reality.
– Physical concepts are free creations of the human mind, and are not, however it may seem, uniquely determined by the external world.
There are far too many giants on whose shoulders we may stand to see the Mirror. Hence we here represent them by a single one, Albert Einstein. Also elsewhere on these pages Einstein appears in the role of an icon for "modern science". "Physical concepts are free creations of the human mind, and are not, however it may seem, uniquely determined by the external world," Einstein and Infeld wrote in Evolution of Physics. "In our endeavor to understand reality we are somewhat like a man trying to understand the mechanism of a closed watch. He sees the face and the moving hands, even hears its ticking, but he has no way of opening the case. If he is ingenious he may form some picture of a mechanism which could be responsible for all the things he observes, but he may never be quite sure his picture is the only one which could explain his observations. He will never be able to compare his picture with the real mechanism and he cannot even imagine the possibility or the meaning of such a comparison."
So we've just heard 'modern science' tell us that the "correspondence with reality" is something that is just simply impossible to verify! And now we'll hear it say that it is also a common result of illusion: "During philosophy’s childhood it was rather generally believed that it is possible to find everything which can be known by means of mere reflection. (...) Someone, indeed, might even raise the question whether, without something of this illusion, anything really great can be achieved in the realm of philosophical thought– but we do not wish to ask this question. This more aristocratic illusion concerning the unlimited penetrative power of thought has as its counterpart the more plebeian illusion of naïve realism, according to which things “are” as they are perceived by us through our senses. This illusion dominates the daily life of men and animals; it is also the point of departure in all the sciences, especially of the natural sciences.”
But if our task is to distinguish what is "really true" from illusion – how can we conduct it based on a criterion (correspondence with reality) which cannot be verified? And which is itself commonly a product of illusion?
– [The] flow from the theoretical to the conventional is an adjunct of progress in the logical foundations of any science.
"We are not discovering an objective picture of reality. We are constructing (an approximate representation of) reality". This conclusion, which we are calling the constructivist credo, follows from the results reached in a broad variety of disciplines (physics, biology of perception, cognitive science, linguistics, sociology, philosophy...). It is also an epistemological position upheld explicitly or implicitly with astonishing consistency by the 20th century's giants.
But there is a problem. When the constructivist credo is placed into a system of thought where "truth" means "correspondence with reality" (and each statement is supposed to be about reality), the result is a paradox.
Fortunately, there is also a natural solution. It is what Willard Van Orman Quine called truth by convention. truth by convention is the kind of truth that mathematics is founded on. "Let x be... Then..." It is meaningless to argue whether x "really is" as stated. In "Truth by Convention", Quine argued that "every science" progresses from an assumption of mutual understanding based on the reality of the shared concepts and ideas, to understanding that such an assumption cannot be upheld, and then resorting to explicit definition by convention.
So why not allow knowledge work at large to progress similarly?
A practical way to do that is to spell out the rules (the underlying epistemological assumption and criteria), by stating them as a convention. We have done that exercise; the result is a prototype called the Polyscopic Modeling methodology. The results achieved by this prototype demonstrate that when the constructivist credo is stated as a convention, it becomes a solid foundation for a an approach to knowledge that satisfies both the logical (consistency) and pragmatic (usefulness) criteria!
And since knowledge federation has originated as, and to a large degree still is motivated by the potential of "digital technology" to "help make this a better world" (see Federation through Stories), the following must also be emphasized: When the contemporary media technology is applied to merely (and radically!) increase the efficiency of the traditional patterns in knowledge work, what the people are already doing, the natural result is information glut; when, however, we are allowed to reconstruct what knowledge work is "from scratch" (based on the available epistemological insights, and the contemporary needs of people and society), then far more innovative and dramatically more useful ways to develop and apply the technology become readily available. But that is exactly what the knowledge federation prototype is there to show.
Once we acknowledge as legitimate the view that the scientific language and method have been our own creation, and that they have limited what we are able to see and assert, it becomes legitimate to also create a language and a method that allows us to see and say more.
The “i” in the above metaphorical image, composed of a circle on top of a square, renders the information that Knowledge Federation undertakes to create in a nutshell. The purpose of this information is to provide direction-setting high-level insights (represented by the circle), based on a multiplicity of lower-level insights (represented by the square), which illuminate an issue or phenomenon from multiple sides.
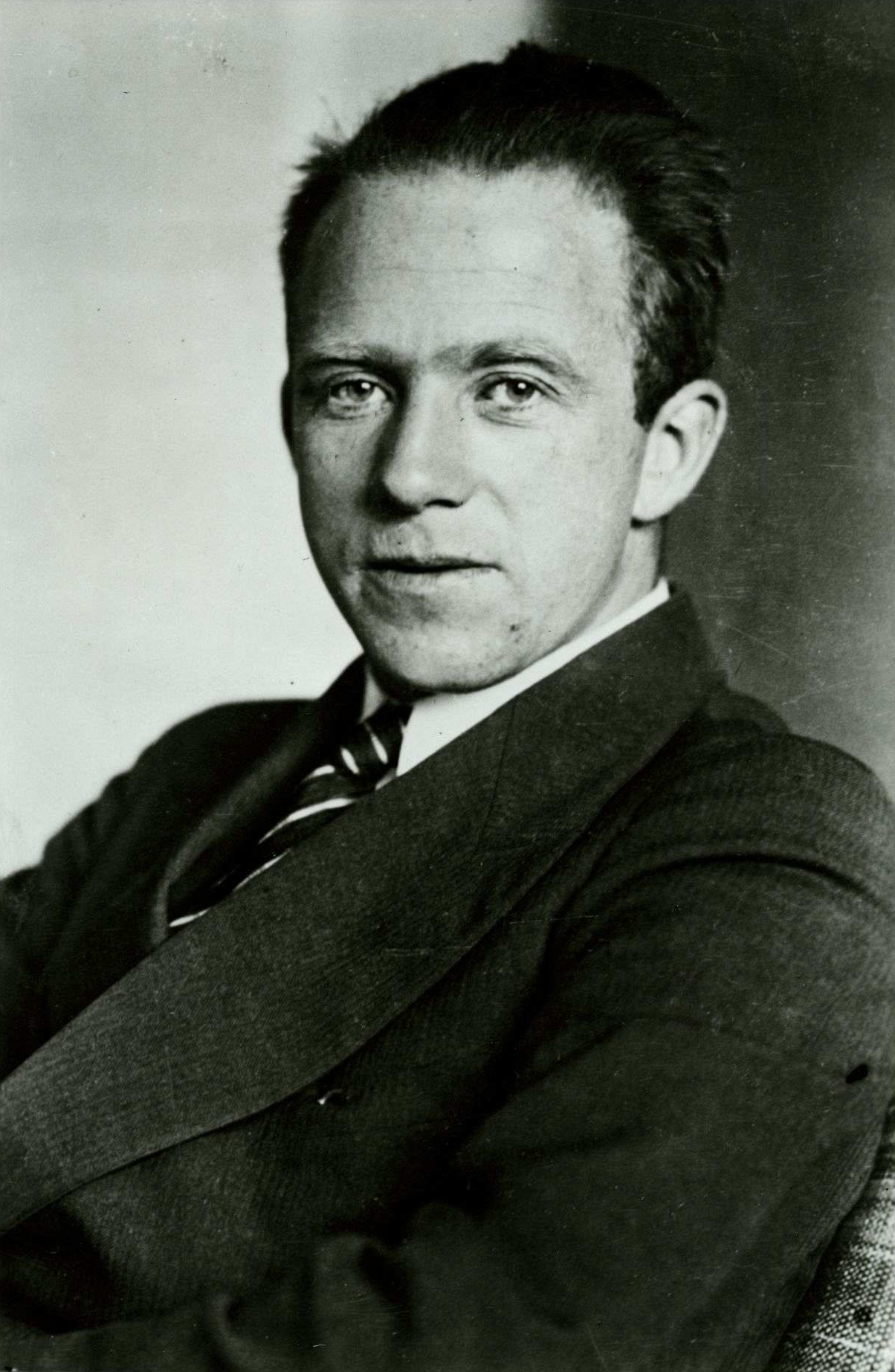
– [T]he nineteenth century developed an extremely rigid frame for natural science which formed not only science but also the general outlook of great masses of people.
In his 1958 book-essay "Physics and Philosophy" Werner Heisenberg explains how... A longer version of Heisenberg's quotation. "One may say that the most important change brought about by [the results of modern physics] consists in the dissolution of this rigid frame of concepts of the nineteenth century", Heisenberg concluded. The point is – we have an *obligation* to correct the error – give the society a more broad and solid foundation for the creation of truth and meaning.
– Whatever we cannot speak of, we need to be silent about (find proper quotation).
Although it belongs to Tractacus, I quote it here as his key point, developed later in Philosophical Investigations .
– Short Whorf's quotation.
Longer version of Whorf's quotation. Point by point, this quotation diagnoses the entire situation.
– The mind must be available to attend to any theme that presents itself to it.
René Descartes is often "credited" as the philosophical father of the limiting (reductionistic) sides of the scientific method. But what he wrote in his "Rules for the application of the mind" (unfinished and published posthumously – might be considered his testament) shows that he would rather be remembered as a supporter of polyscopy. And in the explanation he wrote "Spell it out..."
Ingress.
POINT first...
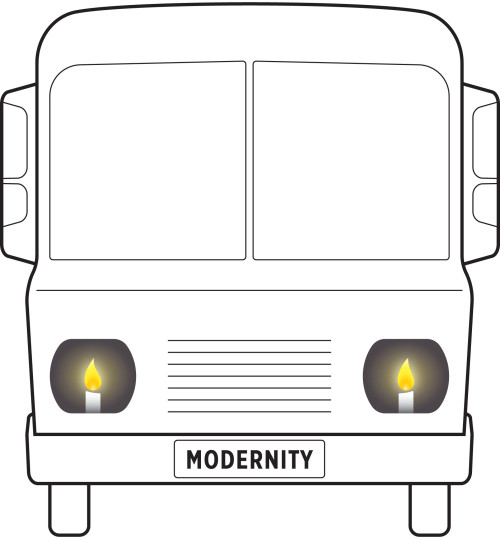
The bus represents our technologically advanced and fast-moving civilisation. The candle headlights represent the way information is created and used, which we have indiscriminately inherited from the past.
As a practical message, this image suggests that the ways of creating and sharing information we have inherited will not fulfil some of the purposes we now urgently need to take care of, notably the purpose of orienting our choices, or of 'illuminating the way'. By designing instead of inheriting what we do with information, suggests this image, we can now make the difference between a hazardous ride into the future, and using our technology to take us to places or conditions where we may justifiably wish to be.
In an academic or fundamental sense, the bus metaphor is pointing to an epistemological stance where information is no longer considered an objective image of reality, but as a part of this reality, or a system within a system, whose purpose is to fulfil certain specific roles. Under this epistemology, the creative acts to reconfigure what we do with information become basic research – as “the discovery of natural laws” has been in traditional science. The bus metaphor further points to the necessity of what we are calling systemic innovation, where we apply our creative capabilities, and our technology, to fulfil the purposes that must be served, rather than to reproduce the habitual practices and ways of working. The bus points to the need to turn our basic institutions or socio-technical “candles” into “lightbulbs”, and to the opportunity to invent and create on this larger, systemic scale. By doing that, suggests the bus metaphor, we may make a similar difference in the ream of our institution as the conventional innovation made by designing technical objects, since the age of the candle.
The task of Knowledge Federation is to prototype and evolve a socio-technical 'light bulb'.
The “i” in the above metaphorical image, composed of a circle on top of a square, renders the information that Knowledge Federation undertakes to create in a nutshell. The purpose of this information is to provide direction-setting high-level insights (represented by the circle), based on a multiplicity of lower-level insights (represented by the square), which illuminate an issue or phenomenon from multiple sides.
What is being shared here – and you may watch it evolve and emerge through time – is the third book of the Knowledge Federation Trilogy titled "Knowledge Federation" and subtitled "Science for the Third Millennium". The idea is to render an academically sound and convincing argument – in an entertaining and engaging cartoon-like format – that "science" (what we collectively rely on to provide us truth and meaning) must become something entirely different than what it presently is.